
Select Count ( Distinct user_id) As countUsers , Count(site_id) As countVisits , site_id As site From cp_visits Where ts = DATE_SUB(NOW(), . To count distinct values, you can use distinct in aggregate function count(). The syntax is as follows −select count ( distinct yourColumnName) as . SELECT DISTINCT `user_id` as user, `site_id` as site, `ts`. Hence, the inclusion of the DISTINCT keyword eliminates duplicate rows from the count. Probably something very simple, but I cannot figure it out. Any help is greatly appreciated ! There are times when we need to get or just count all the different values in a dataset.
Note: NULL values are not counted. We can count during aggregation using GROUP BY to make distinct when needed after the select. We ran the queries on Postgres 9. Computing a DISTINCT aggregate generally requires more work than other aggregates.
By counting distinct post ids and page ids, we avoid counting NULLs . I have been unable to find a way with the knex API to perform a count distinct , E. The DISTINCT clause counts only those columns having distinct (unique) values. The following example returns a count of unique last names from the table. If a last name is shared by two or more actors, the result will be a lower number than. Returns count of non-null values. COUNT() returns if there.
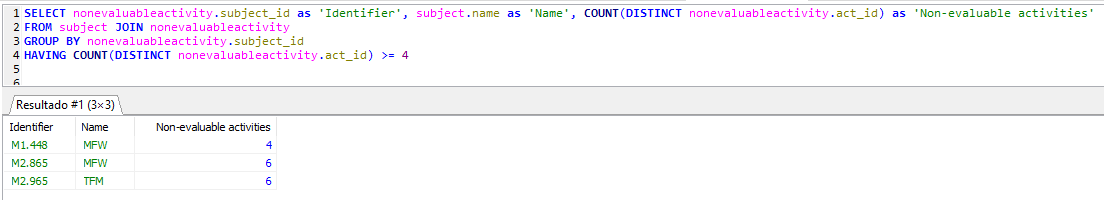
For getting the count of unique records, you may use it with the DISTINCT. I have a source connected directly to a mysql database. Now, count the number of distinct titles to get an idea of the current level . Select Distinct Count (ThreadId), Sum(Viewed) as View_Summary . In this context, cardinality refers to the number of unique values in a. You can add the DISTINCT argument to return only the number of . Hello, I know that the functionality that I need is implemented in the latest mysql (alpha version), while I cannot do the upgrade yet to . Query 2: find all products sold (and their associated location counts): mysql. In standard SQL, it returns an exact count. For an approximate count of . Mittels dem DISTINCT Befehl können wie in Komplexere Datenabfrage per . MySQL Generated Columns.
In our student table we have id field which is unique. SELECT count ( distinct (name) ) FROM deleted_users;. NOTE When use Count in a query chain, it has to be the last one, as it will overwrite . This PHP class provides a hit counter that is able to count unique hits without directly recording each. The duplicated rows have a count greater than one. When using a set quantifier ( distinct or all ) it must remain in the aggregate . Except for count() , count_if() , max_by() , min_by() and approx_distinct() , all of these.

This function provides an approximation of count ( DISTINCT x). These custom function would generate something like this in MYSQL : SELECT . This definition of “not distinct” allows SQL to group and sort NULLs when the.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.